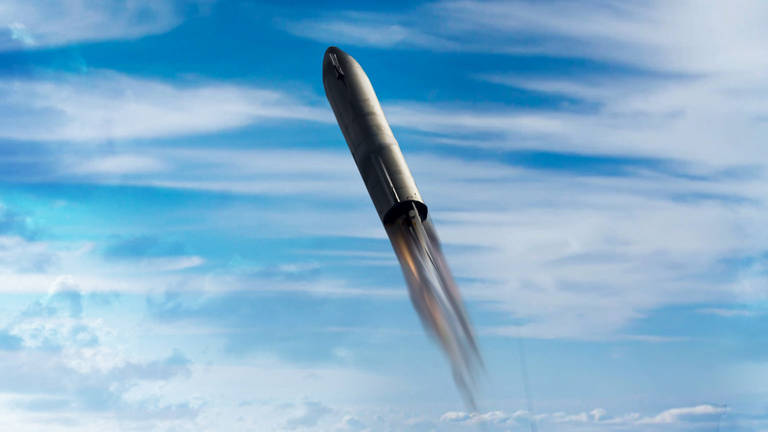
SpaceX recently made rapid strides with the new prototype of the Starship rocket. SpaceX has been pumping out Starship after Starship, and at this point it appears the testing and regulation process is the main hurdle as opposed to the actual construction process. How does SpaceX manage to develop and build the Starship rockets so rapidly?
The first major obstacle when it comes to building a rocket is sourcing funding. We do not know if SpaceX is actually profitable, as they do not release their financial reports like public companies. It is possible that they are in a position where they can choose profitability. However, It is very likely that they take all the profits from commercial launches and put it back into research and development.
Considering that SpaceX is by far the most popular commercial launch provider, it is likely to divert a lot of these profits to Starship. Aside from internal profitability, SpaceX has spent nearly two decades at this point, proving their ability to innovate and their reliability. As a result, it is very easy for SpaceX to raise more money whenever they need. Just last week reports suggested that SpaceX raised another 850 million dollars with a massive valuation of 74 billion.
Something else to keep in mind is that the founder and majority stakeholder is, of course, Elon Musk, who is hovering between richest and second richest person in the world. So investors into SpaceX really do not have to fret about SpaceX going bankrupt. In worst case scenario, Elon will just go ahead and liquidate a bunch of Tesla shares to keep SpaceX afloat.
Of course, SpaceX may be profitable themselves. They have a proven track record and they have massive investor credibility. Thus, for all realistic purposes, they have unlimited funding power. But just because they have so much funding does not mean that they are careless with it.
SpaceX's choice of material with Starship
For the entirety of our space exploration history, virtually all major rockets have used aluminum, titanium, or some sort of carbon composite. This was originally going to be the case with Starship as well. But at the beginning of 2019, SpaceX decided that stainless steel was actually a better choice for a variety of reasons. Starting with, of course, cost.
Elon Musk explains that carbon fiber costs 135 dollars per kilogram and unfortunately, 35% of that is usually wasted in the construction process. So, each kilogram of carbon fiber that ends up making its way onto the final rocket actually cost upwards of $200.
Meanwhile, stainless steel only cost three dollars per kilogram. Aside from the obvious cost savings, this is extremely beneficial. Because it allows SpaceX to experiment much more freely. Instead of running simulations on a computer, where unknown variables do not play a factor, SpaceX can go ahead and just run a real live pressure test till failure. Evidently, the extremely cheap material choice allows SpaceX to run more tests, collect more real data, and rapidly improve as mistakes do not cost them an intolerable amount.
Moving on, stainless steel is also much more durable than carbon fiber. Elon Musk revealed that aluminum and carbon fiber are generally able to withstand 150 to 180 degrees celsius. You might be able to push it to 200 degrees celsius but that's generally the limit. With stainless steel, on the other hand, must suggest that it is capable of temperatures up to 120 to 870 degrees celsius. This is, again, quite important as rockets need to be able to handle very high and very low temperatures during flight.
Moreover, one of the most serious issues with constructing and refurbishing the space shuttle was the heat shield. Every single heat shield tile had to be individually inspected and repaired. This was especially time intensive and tedious because the space shuttle had over 21,000 heat shield tiles. Conversely, since Starship's exterior itself is much more capable of higher temperatures, SpaceX does not have to pay nearly as much attention towards heat concerns.
Elon Musk has even suggested that transpiration-based cooling may be enough to keep Starship cool. In such a system Starship would have two exterior stainless steel layers, and water or cooling liquid would flow between the two sandwich layers. This system is no doubt much easier than installing thousands of heat shield towels which brings down the construction time quite substantially.
Next up we have SpaceX's actual construction process itself. Usually, rockets are constructed in extremely clean environments with large dedicated machinery that takes care of a lot of the work. Although this is quite helpful, this also adds a lot of work. Engineers not only have to design and maintain the rocket itself, but they also have to design and maintain a machine that builds a rocket. Similarly, the rocket company will not only have to fund the rocket itself, but also the machines that assemble and construct various rocket parts.
With Starship, however, this is not the case. SpaceX does not use large molding machines or huge 3D printers to produce parts for Starship. The production process is just making a bunch of stainless steel rings, a couple of flaps, and the nose cone. And as for the construction, most of the construction takes place in broad daylight exposed to all of the elements.
Prototypes often endure rain high winds and even tropical storms, as Boca Chica is right next to the ocean. Also aside from the massive cranes that are used to move and lift components, there is absolutely no fancy machinery. It is literally just a bunch of guys, welding together stainless steel rings out in the open. SpaceX does not even take advantage of spiral welding, because the exterior wall of Starship is not uniformly thick. Although there are some safety concerns regarding this construction process, as it is yet unclear how durable these rockets are. Nonetheless, This rudimentary production and construction process cuts down overall manufacturing time significantly.
Another major method SpaceX utilizes to shorten development and manufacturing time is iteration. SpaceX has been a huge fan of the iterative design process, and this has saved them insurmountable time. Most companies in any industry will segment out the development process. For instance, if we are looking at the airline industry, Boeing will first go ahead and fully design an airplane. This process often takes years. Next they will construct it, test it, and fix any issues. if everything goes well, they will mass produce it and sell it to the airlines. Maybe a few years later, they will go back and modify certain things about the airplane and create version 2 and version 3 and so on.
Between each of these versions though, every single airplane that comes out of Boeing is identical. With SpaceX, on the other hand, no two rockets they produce are identical. SpaceX does not aim to get perfect on the first try, and they definitely do not wait to make future iterations until they get it perfect. With Starship, SpaceX has taken this philosophy to the next level. They think of a design, they put it together as fast as possible, and they launch. If it works, they will focus on how to make it even better. If it does not work, they did not spend too much time and manpower on the launch anyway.
By employing this aggressive development process, SpaceX is able to rapidly filter through what works and what does not work. Elon Musk has confessed that this occasionally results in massive setbacks for the company. However, he has also suggested that SpaceX is willing to tolerate such losses in order to embrace the iterative design process. Once Starship becomes a commercial rocket which people actually use on a regular basis, SpaceX will no longer be able to use this approach, as the stakes would be too high. Considering this, SpaceX is determined to take full advantage of the iterative process while they still can. And a plethora of prototypes is simply a byproduct of this approach.
The final and the main reason SpaceX is able to build starships so quickly is because they are on a constant time crunch. The truth is Elon Musk is running out of time. Elon Musk is actually running out of lifetime and life is unpredictable. Elon Musk is already about to turn 50 this summer, and It took SpaceX nearly 20 years just to get people to the international space station.
Although that is an outstanding achievement, there's still so much work left in actually getting to Mars. At this rate, Mars is simply not going to happen within his lifetime. Elon Musk has even gone on record stating that this is what concerns him most. As a result, he is willing to do anything that's not illegal, or puts people in danger to expedite the development process. If that means building a plethora of prototypes by working 24/7 and blowing several of them up during testing, that's completely fine.
In the end, there are several objective factors that are pushing forward Starship development at unprecedented rates. SpaceX has wisely chosen a great material, crafted a simple construction process, and they have employed an aggressive development strategy. On top of this, they also have essentially unlimited funding and respectable competition nudging them forward. But the biggest factor launching Starship development to Mars is that Elon Musk is on time crunch and he is determined to reach Mars before it is too late.